

April's sluggish job growth and unemployment spike signal looming U.S. recession.
Recent job growth numbers from the U.S. Labor Department indicate potential warning signs for the economy. The figures for April revealed that job growth totaled a mere 175,000 compared to the anticipated 240,000, falling significantly short of consensus estimates. This disappointing data has reignited concerns about a potential recession, as the unemployment rate saw a slight rise to 3.9%.
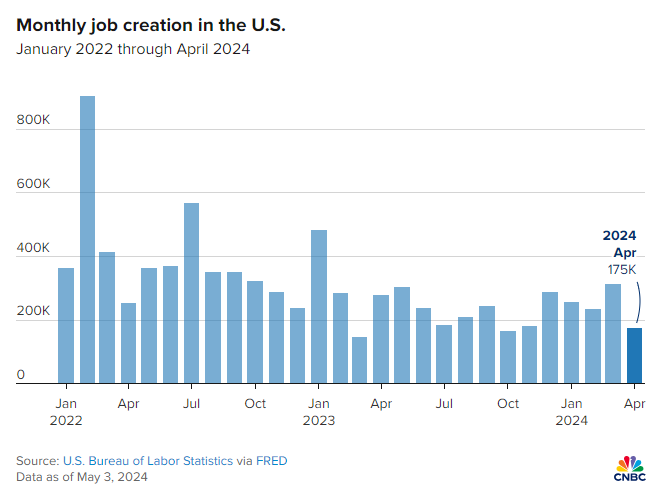
Analysts are paying close attention to the SAHM (Sahm Rule Recession Indicator), which measures the three-month moving average of unemployment against its position over the past twelve months. An increase in the unemployment rate by 50 basis points relative to this average is seen as a strong indicator of a recession. As of April, unemployment has increased from 3.4% to 3.9% over the preceding year, hitting the critical 50 basis point threshold that suggests the economy may already be experiencing a downturn.
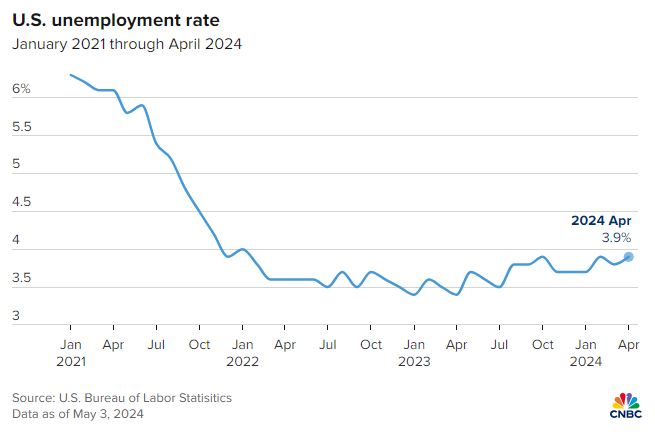
The U6 unemployment rate, a more inclusive metric that counts those marginally attached to the labor force and those employed part-time for economic reasons, climbed to 7.4%, the highest since November 2021. This rate is considered by some economists as a more accurate reflection of the labor market's health.
Sector-wise, healthcare led in job creation with an increase of 56,000 positions, followed by gains in social assistance, transportation, warehousing, and retail. These trends align with demographic shifts in the U.S. and changes in consumer spending patterns.
Following the release of the employment data, markets responded by pricing in a strong likelihood of interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. This move has had an inverse effect on the stock market, where typically negative economic news has led to a rise in stock prices due to expectations of monetary easing.
Further analysis suggests disparities in wage growth, with younger age groups (16 to 24) seeing larger percentage increases in wages compared to older demographics, skewing the overall wage growth data. This discrepancy raises questions about the real economic impact on average American households, particularly in the face of rising inflation.
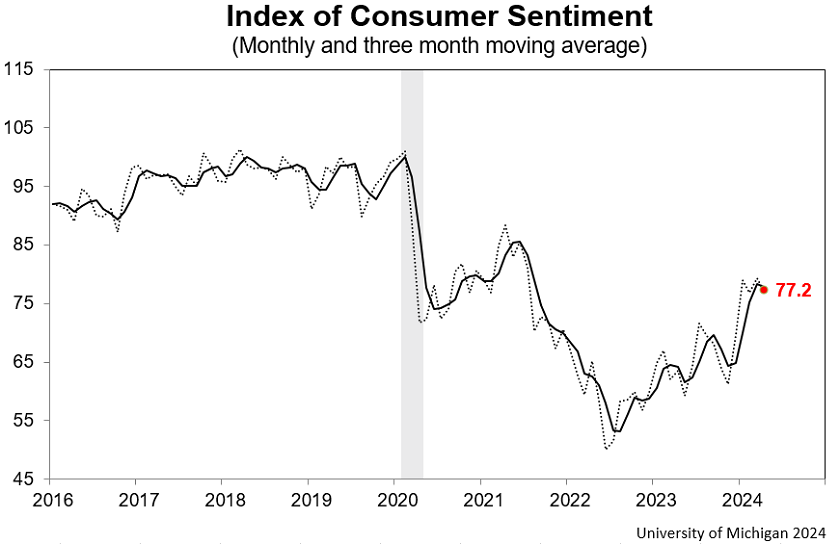
The broader economic sentiment remains cautious, as evidenced by consumer sentiment surveys like the University of Michigan's, which, despite recent improvements, still lingers below pre-pandemic levels. This suggests a disconnect between the perceived strength of the economy and the actual experience of consumers, especially when considering indicators like earnings misses from major consumer brands, which signal potential stress on the consumer base.
The recent jobs report has thrown a spotlight on the underlying fragility of the U.S. economy. With the U6 unemployment rate on the rise and the SAHM recession indicator nearing its critical threshold, the possibility of a recession looms larger. Despite this, the stock market continues its paradoxical rally on expectations of policy intervention.